Spanish Verbs
Agitar Conjugation
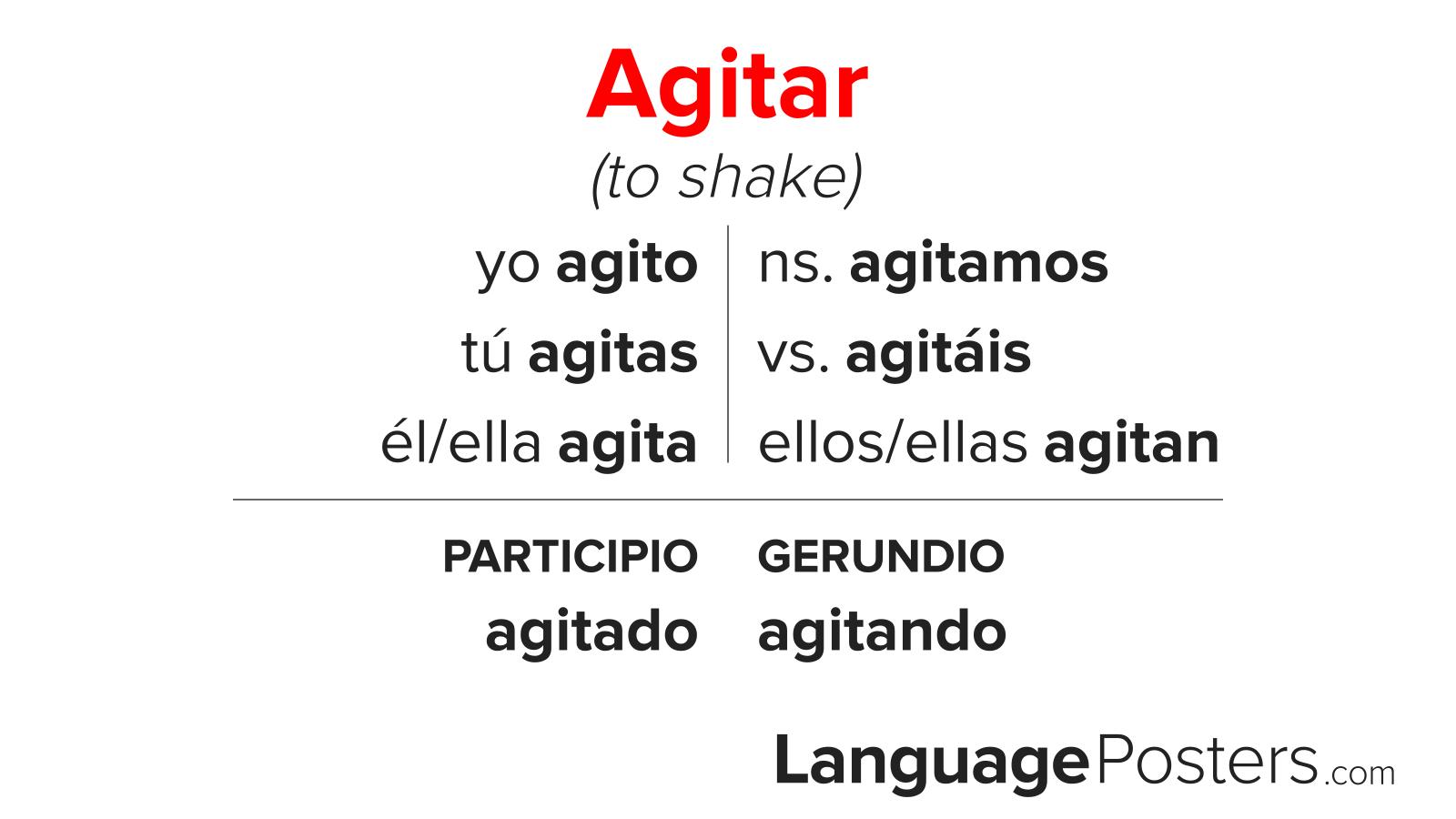
Agitar is a Spanish regular AR verb meaning "to shake". Verbs are considered regular if they follow a predictable pattern when conjugated.
Present Tense
Past Tenses
Future Tenses
Subjunctive Tenses
Further Reading
100 Most Used Spanish Verbs Poster w/ Study Guide
A selection of the most used irregular and regular Spanish verb conjugations. A must have for anyone who wants to learn Spanish!
Agitar Conjugation
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | agito | I shake |
| Tú | agitas | You shake |
| Él/Ella/ |
agita | He/She shakes |
| Nosotros | agitamos | We shake |
| Vosotros | agitáis | You (plural) shake |
| Ellos/ |
agitan | They shake |
* Irregular forms are highlighted in red
Agitar Participio
The Participio or Past Participle of Agitar is agitado. This is used to form the Agitar Present Perfect and the Agitar Past Perfect.
Agitar Gerundio
The Gerundio or Present Participle of Agitar is agitando. This is used to form the Agitar Present Continuous.
Agitar Present Continuous
The Present Continuous (presente progresivo or presente continuo) is used to describe actions that are happening right now or around now. To form the present continuous tense, combine the Estar conjugation with the Agitar Gerundio (or Present Participle).
Example: Él está siendo muy egoísta últimamente. (He is being very selfish lately.)
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | estoy agitando | I am shaking |
| Tú | estás agitando | You are shaking |
| Él/Ella/ |
está agitando | He/She is shaking |
| Nosotros | estamos agitando | We are shaking |
| Vosotros | estáis agitando | You (plural) are shaking |
| Ellos/ |
están agitando | They are shaking |
* Irregular forms are highlighted in red
Back to topAgitar Past Tense
Spanish has several past tenses, each serving a specific purpose to express actions in the past.
Additionally, the use of Spanish past tenses can vary significantly across regions due to cultural and linguistic differences.
These are some of the most commonly used Spanish past tenses:
Agitar Preterite
The Preterite Tense (Pretérito or Indefinido) is used for completed actions in the past that have a clear beginning or end.
Example: Ayer comí pizza. (Yesterday, I ate pizza).
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | agité | I shook |
| Tú | agitaste | You shook |
| Él/Ella/ |
agitó | He/She shook |
| Nosotros | agitamos | We shook |
| Vosotros | agitasteis | You (plural) shook |
| Ellos/ |
agitaron | They shook |
* Irregular forms are highlighted in red
Back to topAgitar Imperfect
The Imperfect Tense (Imperfecto) describes ongoing, habitual, or background actions in the past, often without a defined start or end.
Example: Cuando era niño, jugaba fútbol todos los días. (When I was a child, I used to play soccer every day).
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | agitaba | I used to shake |
| Tú | agitabas | You used to shake |
| Él/Ella/ |
agitaba | He/She used to shake |
| Nosotros | agitábamos | We used to shake |
| Vosotros | agitabais | You (plural) used to shake |
| Ellos/ |
agitaban | They used to shake |
* Irregular forms are highlighted in red
Back to topAgitar Present Perfect
The Present Perfect Tense (Presente Perfecto) is used to describe actions that have been completed recently or have relevance to the present moment. The Present Perfect Tense is formed by combining the Present Tense of the auxiliary verb Haber Conjugation with the Agitar Participio.
Example: He leído ese libro. (I have read that book).
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | he agitado | I have shaken |
| Tú | has agitado | You have shaken |
| Él/Ella/ |
ha agitado | He/She has shaken |
| Nosotros | hemos agitado | We have shaken |
| Vosotros | habéis agitado | You (plural) have shaken |
| Ellos/ |
han agitado | They have shaken |
* Irregular forms are highlighted in red
Back to topAgitar Past Perfect
The Past Perfect Tense (Pluscuamperfecto) refers to actions completed before another action in the past. The Past Perfect Tense is formed by combining the Imperfect Tense of the auxiliary verb Haber Conjugation with the Agitar Participio.
Example: Había comido antes de salir. (I had eaten before leaving).
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | había agitado | I had shaken |
| Tú | habías agitado | You had shaken |
| Él/Ella/ |
había agitado | He/She had shaken |
| Nosotros | habíamos agitado | We had shaken |
| Vosotros | habíais agitado | You (plural) had shaken |
| Ellos/ |
habían agitado | They had shaken |
* Irregular forms are highlighted in red
Back to topAgitar Future Tense
The Future Tense (Futuro) is used to describe actions or events that will happen in the future. It often expresses certainty or plans about what is yet to come.
Example: Mañana comeré pizza. (Tomorrow, I will eat pizza).
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | agitaré | I will shake |
| Tú | agitarás | You will shake |
| Él/Ella/ |
agitará | He/She will shake |
| Nosotros | agitaremos | We will shake |
| Vosotros | agitaréis | You (plural) will shake |
| Ellos/ |
agitarán | They will shake |
* Irregular forms are highlighted in red
Back to topAgitar Conditional Tense
The Conditional Tense (Condicional) is used to express hypothetical situations, polite requests, or actions that depend on other conditions. It is often used in combination with the Future Tense.
Example: Me gustaría un café, por favor.(I would like a coffee, please).
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | agitaría | I would shake |
| Tú | agitarías | You would shake |
| Él/Ella/ |
agitaría | He/She would shake |
| Nosotros | agitaríamos | We would shake |
| Vosotros | agitaríais | You (plural) would shake |
| Ellos/ |
agitarían | They would shake |
* Irregular forms are highlighted in red
Back to topAgitar Subjunctive
The Subjunctive Tense (Subjuntivo) is used to express doubt, uncertainty, desire, or emotion. It is often used in dependent clauses introduced by specific conjunctions or verbs.
Example: Espero que seas feliz. (I hope you are happy).
| Pronoun | Conjugation | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | agite | I shake |
| Tú | agites | You shake |
| Él/Ella/ |
agite | He/She shakes |
| Nosotros | agitemos | We shake |
| Vosotros | agitéis | You (plural) shake |
| Ellos/ |
agiten | They shake |
* Irregular forms are highlighted in red
Back to topSpanish Regular Verbs
A verb is called a regular verb when its conjugation follows a consistent and predictable pattern. In contrast, a verb that does not follow these standard patterns is called an irregular verb. In Spanish, the three regular conjugation patterns are based on the verb endings: -AR, -ER, and -IR.

Spanish Conjugation Chart
Looking for more Spanish verbs like Agitar? Check out our Spanish Conjugation Chart, the 100 Most Used Spanish Verbs Poster!
Back to top

